- Topic
13k Popularity
9k Popularity
40k Popularity
16k Popularity
38k Popularity
16k Popularity
6k Popularity
3k Popularity
112k Popularity
27k Popularity
- Pin
- 🚨 Gate Alpha Ambassador Recruitment is Now Open!
📣 We’re looking for passionate Web3 creators and community promoters
🚀 Join us as a Gate Alpha Ambassador to help build our brand and promote high-potential early-stage on-chain assets
🎁 Earn up to 100U per task
💰 Top contributors can earn up to 1000U per month
🛠 Flexible collaboration with full support
Apply now 👉 https://www.gate.com/questionnaire/6888
- 🔥 Gate Square #Gate Alpha Third Points Carnival# Trading Sharing Event - 5 Days Left!
Share Alpha trading screenshots with #Gate Alpha Trading Share# to split $100!
🎁 10 lucky users * 10 USDT each
📅 July 4, 4:00 – July 20, 16:00 UTC+8
Gate Alpha 3rd Points Carnival Issue 10 is in full swing!
Trade and post for double the chances to win!
Learn more: https://www.gate.com/campaigns/1522alpha?pid=KOL&ch=5J261cdf
- 🎉 [Gate 30 Million Milestone] Share Your Gate Moment & Win Exclusive Gifts!
Gate has surpassed 30M users worldwide — not just a number, but a journey we've built together.
Remember the thrill of opening your first account, or the Gate merch that’s been part of your daily life?
📸 Join the #MyGateMoment# campaign!
Share your story on Gate Square, and embrace the next 30 million together!
✅ How to Participate:
1️⃣ Post a photo or video with Gate elements
2️⃣ Add #MyGateMoment# and share your story, wishes, or thoughts
3️⃣ Share your post on Twitter (X) — top 10 views will get extra rewards!
👉
EO Think Tank 丨 AIGC regulatory situation in China, the United States and the European Union
Source: EO Intelligence
Author: Anjie Shize
Original title: "Global Generative Artificial Intelligence Regulatory Research Report"
Generative Artificial Intelligence Regulatory Map
As of July 24, 2023, we have drawn a regulatory map based on the combing of global generative artificial intelligence regulatory trends:
Red area indicates that a mature and strict regulatory system has been or will be established in this area, mainly including the European Union, Canada and China;
Orange area indicates that there are currently certain restrictions and regulatory requirements on generative artificial intelligence products in this region, such as the United States;
Yellow area indicates that there is currently no relevant system in this region, but regulators plan to formulate rules for generative artificial intelligence in the future, such as the United Kingdom, Australia and India;
Green area indicates that there is currently no relevant system in this area, and regulators also tend not to adopt mandatory regulatory measures in the future, such as Singapore, Japan, and Hong Kong, China.
China
Chinese regulatory agencies have strengthened the supervision of artificial intelligence from 2021, and successively released the "Internet Information Service Algorithm Recommendation Management Regulations" ("Algorithm Recommendation Regulations"), Internet Information Service Deep Synthesis Management Regulations ("Deep Synthesis Regulations") ) and the Interim Measures for the Administration of Generative Artificial Intelligence Services ("Generative Measures") are three important departmental regulations. All three regulations may apply to generative AI services provided to the public in China. In the future, China may also formulate a higher-level "Artificial Intelligence Law" and implement a scientific and technological ethics review system.
At the same time, these three regulations also established that China will adopt the principle of "inclusive and prudent classification and hierarchical supervision". In the future, the relevant national authorities will formulate corresponding classified and hierarchical regulatory rules or guidelines for the characteristics of generative artificial intelligence technology and its service applications in related industries and fields.
At present, the agency responsible for algorithm filing, evaluation and supervision is mainly the Cyberspace Administration of China (Network Management Technology Bureau of the Central Cyberspace Administration of China). At the same time, the telecommunications authorities and public security departments will also be responsible for supervision and management according to their duties.
Key compliance obligations for generative AI:
EU
The EU's current artificial intelligence legislation is still mainly focused on traditional artificial intelligence rather than generative artificial intelligence, but it has gradually touched on the issue of generative artificial intelligence. Obligations of relevant underlying model providers.
The EU's approach to artificial intelligence advocates "human-centric", while promoting the development and innovation of artificial intelligence, it also builds a regulatory system to prevent risks and protect the basic rights and safety of citizens.
The EU's current regulation and governance of artificial intelligence focuses on respecting human dignity, personal freedom, and protecting data and privacy security. The latest legislative development is the revision of the Artificial Intelligence Act by the European Parliament on June 14, 2023. The law adopts a "risk-based approach" (risk-based) to divide artificial intelligence systems into four categories, and establishes different levels of compliance requirements. Among them, generative artificial intelligence systems generally belong to limited-risk artificial intelligence systems and need to comply with minimum transparency obligations, but may fall into the category of high-risk artificial intelligence systems due to their applicable fields and generated content. At the same time, the law also stipulates the compliance obligations of different entities such as providers, importers, distributors, deployers, and providers of basic models related to general and generative artificial intelligence.
According to the nature, severity and other factors of the infringement, relevant parties who do not comply with the "Artificial Intelligence Law" may be imposed administrative fines of different scales.
In terms of law enforcement, in recent years, several EU member states, including Italy, France, and Spain, have launched investigations into ChatGPT.
In terms of regulation, the EU currently does not have an independent agency dedicated to artificial intelligence regulation. It is mainly jointly supervised and enforced by competent authorities in different fields at the EU level and the member state level. The latest draft of the "Artificial Intelligence Law" requires member states to designate one or more competent agencies, including a national regulatory agency, responsible for overseeing the application and implementation of the "Artificial Intelligence Law"; Representatives formed a new EU agency, the "Office for Artificial Intelligence", with a view to providing guidance and coordinating joint cross-border investigations for the uniform application of the "Artificial Intelligence Act". In addition, the European Data Protection Board (EDPB), national market surveillance authorities, customs, and national consumer protection authorities are responsible for AI-related enforcement in their respective fields.
Special obligations of providers of basic models related to general and generative artificial intelligence in the "Artificial Intelligence Law":
** **Transparency obligations in the Artificial Intelligence Act for limited risk AI systems, including generative AI:
**Transparency obligations in the Artificial Intelligence Act for limited risk AI systems, including generative AI:
**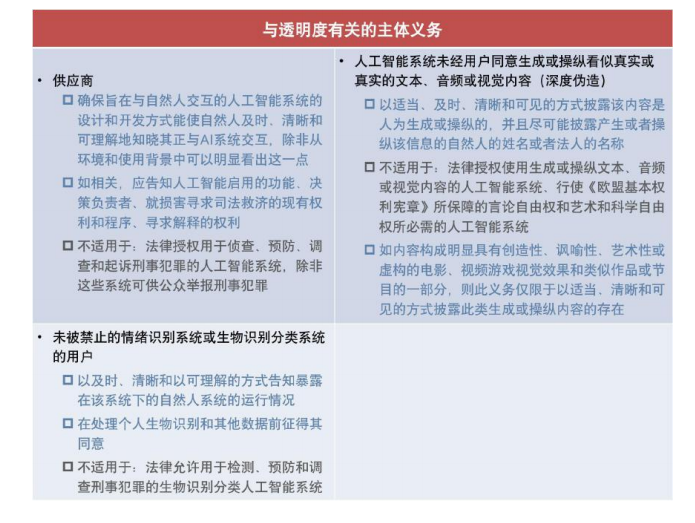 **
**
USA
The United States is the source and leader of artificial intelligence technology. To maintain this leadership, the U.S. government has made promoting innovation and development in AI a high priority.
Therefore, the United States advocates that regulation should aim to promote responsible innovation of artificial intelligence (AI), and should reduce unnecessary obstacles to the development and deployment of artificial intelligence through regulatory and non-regulatory measures, while protecting the technology, economy, and national security of the United States. Core values such as civil liberties, human rights, rule of law, privacy and respect for intellectual property.
Currently, the focus of the United States on artificial intelligence is civil rights, civil liberties, data and privacy security, and intellectual property protection.
Although some states in the United States have passed bills related to artificial intelligence, there is currently no legal document in the United States that specifically regulates general artificial intelligence or generative artificial intelligence. Although lawmakers from both parties are trying to introduce legislation on different AI matters, there is a trend that the regulation of AI in the United States may be strengthened, but federal legislative regulation is still at a very early stage. Non-regulatory measures that are not legally mandatory in subdivided fields, such as policy documents, guidelines, governance frameworks, pilot projects and experiments, industry self-regulation, and consensus of social organizations, etc., are the main references and guidelines for artificial intelligence companies to act in the United States at present. .
It should be noted that the US government has a tendency to implement strict import and export controls on products related to generative artificial intelligence. The U.S. government has severely restricted exports to China of top-tier computing chips, supercomputers and other semiconductors used in artificial intelligence work. In addition, on July 4, 2023, the media reported that the U.S. government also plans to restrict Chinese companies from using U.S. cloud computing services.
Currently, there is no independent agency in the United States that specifically regulates artificial intelligence, and competent authorities in various fields will continue to supervise generative artificial intelligence within their own responsibilities.
For more content of the report, please read the original text: "Global Generative Artificial Intelligence Regulatory Research Report"